Microfinance Meaning - Types, Benefits, History and How It Works

If you lack credit history or collateral but hope to start a business and become financially independent, microfinance loans can make it possible.
Microfinance goes beyond small loans. It empowers individuals, opens doors to opportunity, and supports financial growth. Read on to learn what microfinance is, its types, its benefits, and how it's helping millions globally.
Microfinance: A Smarter Way to Borrow
India's personal loan market is expected to reach USD 77.72 billion in FY2032.
However, not everyone who wants to borrow money can walk into a bank and be approved. On this note, your income and credit score significantly affect your eligibility for a personal loan in India.
A large number of Indian borrowers are ineligible for formal bank loans due to low income, poor credit history, or other grounds. It is for such individuals that microfinance provides small, collateral-free loans.
Also Read: Personal Loan Alternatives - You Should Consider
Microfinance Services Every Borrower Should Know
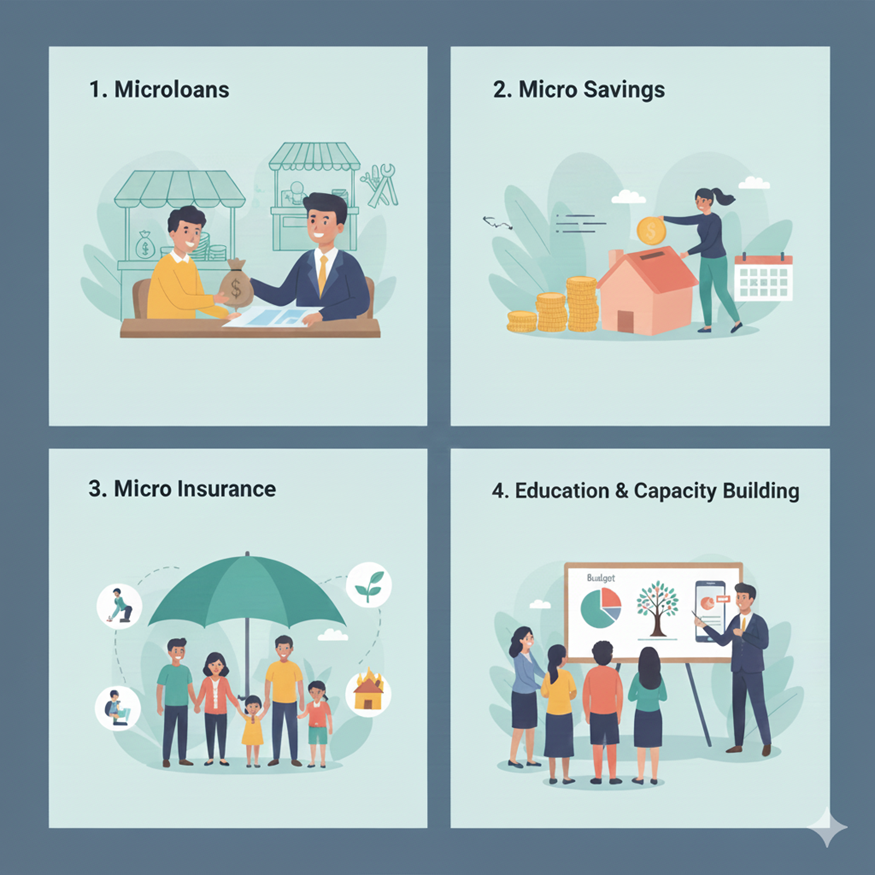

Here are the key microfinance services that can support your financial growth and stability:
1. Microloans or Microfinance Loans (MFL)
These loans help borrowers to
● Start or expand a small business
● Buy necessary tools or supplies
● Sustain working capital
● Manage emergency or unanticipated needs
2. Micro Savings
Micro savings schemes motivate people to save in small quantities frequently, and can help them achieve
● Improved financial discipline
● An emergency fund
3. Micro Insurance
This offers the low-income population affordable protection against life's uncertainties. It covers:
● Health emergencies
● Accidents
● Crop or livestock loss
● Disability or life risks
Even minimal protection can help prevent a financial crisis in families with tight budgets.
4. Education & Capacity Building
Microfinance is also about helping people use money wisely. Many MFIs offer training to borrowers on:
● Budgeting and household financial management
● Starting and expanding a small business
● Utilising digital payment systems
● Borrowing responsibly
Benefits of Microfinance to Explore
Microfinance has a host of benefits, especially in developing economies like India.
Creates Economic Empowerment
A microfinance loan can make a huge difference in a person's ability to generate income.
● Microfinance gives people the chance to grow financially and achieve long-term security.
● Consider the vegetable seller who buys a larger cart, or the home baker who upgrades to a better oven. Their daily income increases.
Brings Financial Inclusion
Microfinance extends credit to individuals who traditional channels would have denied based on their credit score or income.
Helps Break the Cycle of Poverty
The ability to borrow even small amounts can raise incomes, help families manage emergencies more effectively, and reduce dependence on moneylenders who charge exorbitant interest rates. Higher income means better education, nutrition and security.
Supports Women Entrepreneurs
99% of India's 8.67 crore MFI clients are women. It highlights how women are finally gaining financial independence through microfinance, making meaningful contributions to their homes and communities.
Also Read: Instant Personal Loan for Housewife: How to Apply Easily
Flexible Credit Repayment
Microfinance loans have
● Lower interest rates than informal money lenders
● Easier, more flexible repayment plans
This ensures that loans don't place undue stress on household budgets or the financial health of borrowers.
Strengthens Borrower's Credit Profile
Regular repayments on a microloan build your credit history. For many taking a loan for the first time, this serves as a prelude to easier loan approval and better opportunities, such as vehicle, home, or business loans.
How Does Microfinance Work?
Here's a breakdown of how the microfinance process works:
Step 1: Finding the Right Borrowers
It begins with MFIs selecting individuals or self-help groups (SHGs) that are usually left out of conventional loans, such as small vendors, daily wage workers, or women business owners.
Step 2: The Power of Group Lending
A large number of MFIs employ a so-called joint-liability mechanism, in which 5–10 borrowers form a group. Every individual is accountable for the group's payment. It is this community-based lending model that reduces risk in the long run.
Also Read: Split Payments: What is it, Methods, How Does it Work & Uses
Step 3: Loans Without Collateral
Borrowers don't need fixed deposits or property papers to avail a microfinance loan. Their ability to repay determines whether they qualify.
Step 4: Simple Eligibility Check
Instead of filling out complex bank forms, MFIs focus on simple factors: income level and repayment ability.
Step 5: Direct Loan Disbursement
When the loan is approved, the amount is credited into the borrower's bank account or digital wallet. Repayments are made through weekly or monthly EMIs.
Wondering if you qualify for a loan? Find out in seconds with our loan eligibility calculator!
Microfinance Loan Eligibility & Application Process in India
Here's a snapshot of everything you need to know before applying for a microfinance loan:
Eligibility
● Stable income
● A part of the low-income or underserved segments
● No major outstanding loans
Documents Required
● Aadhaar and PAN (optional)
● Address proof
● Recent photo
● Bank passbook
How to Apply
Borrowers can apply through:
● MFIs or Non-Banking Financial Institutions (NBFC)
● Instant Loan Apps
The process is simple and usually completed within 1–3 days.
Microfinance Loans: Helping Dreams Take Shape
Microfinance empowers families and communities, providing confidence, long-term security, and opportunities for income generation.
Hero FinCorp is a leading Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) in India, offering a wide range of financial products, including business loans, unsecured personal loans, loyalty loans, and general insurance.
Enjoy a quick, paperless application process and flexible repayment options. Download our instant loan app to apply for a loan today!
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
How are microfinance and traditional bank loans different?
Microfinance loans are generally smaller amounts and do not require collateral. Banks need documents, credit scores, and collateral for loans.
Who can apply for a microfinance loan in India?
Small business owners, daily wage earners or anyone unable to get loans through formal banking.
How are interest rates for microfinance loans determined?
Interest rates may vary depending on the MFI, operational cost, loan size and borrower profile.
Can I use a microfinance loan for personal benefit?
No, they are generally used for income-generating activities. However, a few MFIs may offer personal-use loans.