Personal Loan Alternatives - You Should Consider

Personal loans are extremely versatile. But sometimes, even they might not help. Quite possibly, the interest rate feels too high, or the paperwork seems never-ending. That’s where personal loan alternatives come in. They can be easier, faster, and often more flexible options to borrow money when you need it.
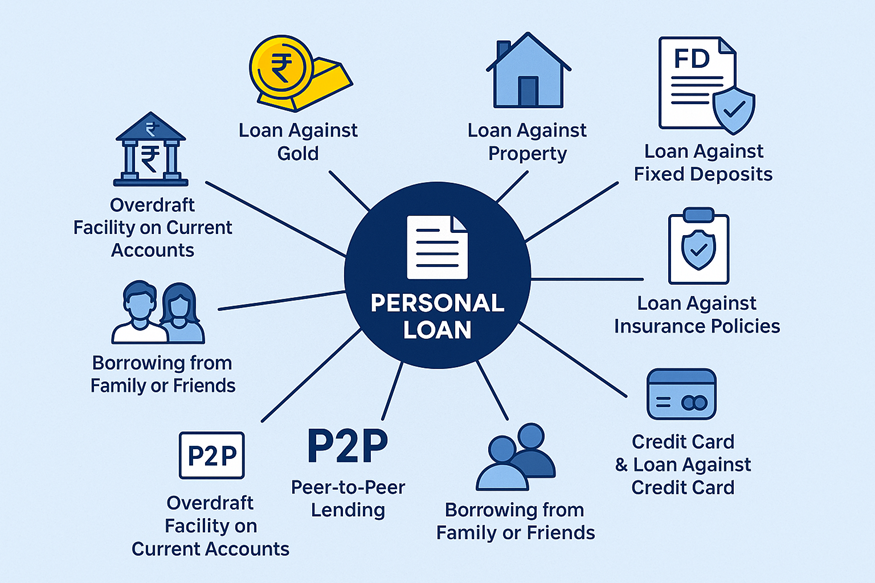
These alternatives can include things like gold loans, property loans, or even borrowing against your savings. Let’s look at why exploring these alternatives might be worth your while.
Why You Should Look for Personal Loan Alternatives
Personal loan alternatives are ways to borrow money other than a traditional unsecured personal loan. There are good reasons to explore them:
● You can get lower interest rates than most personal loans.
● They often have easier approval, even if your credit score isn’t perfect.
● Some options don’t affect your credit score right away.
● Assets, like gold or property, unlock money quickly.
● Many offer flexible repayment plans to fit your budget.
Top Personal Loan Alternatives in India
You’ll find several alternatives to personal loans in India. Each personal loan alternative is suited for different needs and profiles. Here’s a closer look:
Loan Against Gold (Gold Loans)
You pledge gold jewellery or coins as security and get cash instantly, often up to 75% of the gold’s value. Interest rates are lower than those of unsecured loans, and processing is quick. Perfect for those needing emergency funds without credit history checks. However, defaulting means risking your pledged gold.
Loan Against Property (LAP)
If you own a home or commercial space, you can borrow against it. They unlock higher loan amounts (as much as 70-80% of the property’s value). You may also get longer repayment tenures and lower interest rates. But the paperwork can take time. LAP is more suitable for big-ticket expenses like education, medical bills, or business expansion.
Loan Against Fixed Deposits (FD Loans)
Banks and NBFCs allow you to borrow against your FD without breaking it. Typically, you can get up to 90% of the fixed deposit value. Interest is usually just 1-2% higher than your FD rate. Best for those needing short-term liquidity without losing FD interest earnings.
Loan Against Insurance Policies
If you have a traditional life insurance policy, you can borrow against its surrender value. The process is straightforward, and interest is generally lower than that of personal loans. However, not all policies qualify, and missing repayments can reduce your policy’s maturity benefit.
Credit Cards and Loan Against Credit Card
Credit cards double up as mini-loans with instant access to funds. Some banks also offer loans against your existing credit limit. They’re great for short-term needs but can become costly if balances aren’t paid off quickly.
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Lending
Online P2P platforms connect borrowers directly with investors. Interest rates vary by credit score, but the process is 100% digital and quick. It’s useful for those who may not qualify for bank loans, though repayment discipline is key.
Also Read: Small Personal Loan or Mini Loan: How Are They Different?
Overdraft Facility on Current Accounts
If you’re self-employed, your bank may offer an overdraft on your current account. You pay interest only on the amount you use. It’s excellent for managing cash flow, though the facility depends on your business turnover.
Also Read: Overdraft Facility Meaning, Features, and How it Works
Borrowing from Family or Friends
This is the oldest and simplest personal loan alternative. Borrowing from loved ones can save you from paperwork and interest. That said, your personal relationships may suffer. Just make sure to set clear repayment terms to avoid misunderstandings.
Benefits of Choosing Hero FinCorp for Instant Personal and Alternative Loans
Hero FinCorp makes borrowing simple and transparent, whether it’s a personal loan or an instant personal loan alternative. You get:
● 100% digital application process, no branch visits.
● Quick approvals with same-day disbursals.
● Competitive interest rates with flexible EMI plans.
● Trusted NBFC with strong customer support and transparent policies.
Want a loan that fits your life, not the other way around?
Apply for a Hero FinCorp personal loan or explore smart alternatives online today.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the best alternatives to personal loans in India?
Secured loans against gold, property, and fixed deposits are popular alternatives to personal loans in India.
2. Can I get an instant loan without collateral?
Yes. NBFCs like Hero FinCorp offer quick personal loans without security.
3. How do gold and property loans differ from personal loans?
They’re secured loans. Here, your asset acts as collateral for the loan.
4. How does my credit score affect eligibility?
Higher credit scores unlock better terms, but secured options are available even with low credit.
5. Can I switch from a personal loan to a secured loan alternative later?
Yes, refinancing is possible if you have eligible assets or collateral.