Business Economics: Meaning, Nature, Scope and Types

No market remains constant. Expenses can increase, demand can slow, and customer behaviour rarely stands still. Despite that, production and pricing decisions cannot be postponed.
Business economics provides a way to think through these choices using evidence rather than assumptions. It supports better resource use and more deliberate planning.
To understand its role clearly, we need to start with its meaning.

Understanding the Meaning of Business Economics
Business economics brings economic thinking into the routine decisions of a business. It supports everyday calls on prices, production and spending by relying on actual figures.
Changes in the market show up in sales numbers, costs and cash flow. That’s where managers feel the impact. That perspective helps management stay steady even when conditions change.
Core Principles and Features of Business Economics
Business economics is not abstract. It is closely linked to daily management work and the decisions that keep a business running. Its main features include:
- Microeconomic focus: The emphasis stays on individual businesses and the choices they make about prices, output and managing costs
- Use of economic theory: Familiar ideas such as demand, supply and competition are used as reference points when decisions are taken
- Data-based analysis: Managers look at actual figures and past results before planning ahead
- Problem-solving approach: It helps address everyday concerns such as managing expenses and allocating resources carefully
- Future orientation: It considers expected changes in demand, competition and wider economic conditions while planning
Also Read: Manpower Supply Business in India
Bridging Theory and Business Practice
Applying economic theory in business simply means using structured reasoning when making decisions. Pricing, production planning and expansion plans are often reviewed with the help of cost analysis and demand estimates.
Normative, Prescriptive, and Decision-Orientated Nature
Business economics looks at what is happening in the market and then considers how a business should respond. Some parts focus on facts and data. In the end, someone has to decide.
When funds are tight and demand is uncertain, managers go back to the figures. They look at likely sales, expected costs and possible returns before acting.
The Broad Scope of Business Economics
Business economics comes up in everyday management work. When prices are reviewed, when costs are rising, when investment plans are discussed, economic reasoning is part of the conversation. But managers also have to watch what is happening outside the company, new regulations, stronger competitors, changes in the economy.
Looking at both the inside numbers and the outside signals keeps decisions from becoming short-sighted.
Operational Issues in Business Economics
- Demand analysis: Studies customer demand to estimate sales and predict future trends
- Production analysis: Looks at how resources are used to produce goods or services efficiently
- Cost analysis: Reviews fixed and variable expenses to understand where money is being spent
- Pricing policies: Sets prices after looking at demand, operating costs and competitive conditions
- Capital budgeting: Assesses major investment decisions before allocating financial resources
Also Read: Annual Budget: Your Guide to Annual Financial Planning by HeroFinCorp
Environmental or External Issues in Business Economics
- Economic environment: Refers to wider economic conditions such as rising prices, lending rates and growth levels
- Business cycles: Follows the economy’s ups and downs and how they affect demand
- Government policy: Accounts for tax structures, regulatory updates and trade rules shaping operations
- Market structure: Examines the level of competition within the industry
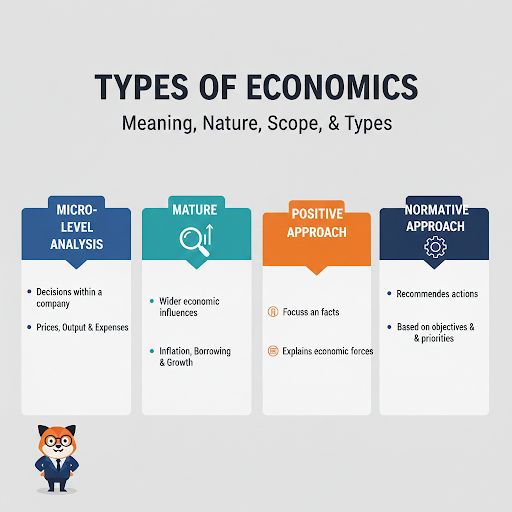
Different Types of Business Economics
The types of business economics can be grouped by the way business problems are examined and interpreted. Key types include:
- Micro-level analysis: Centres on the decisions taken within an individual company, including prices, output levels and expenses
- Macro-level analysis: Considers wider economic influences like inflation trends, borrowing costs and national growth
- Positive approach: Focuses on facts and explains how economic forces operate
- Normative approach: Recommends actions based on business objectives and priorities
Microeconomics and Macroeconomics in Business
Micro business economics deals with decisions made within a single company or industry. At the company level, attention is given to demand patterns, pricing choices and cost control. Macro business economics examines broader economic conditions such as inflation, public policy and overall income in the economy.
Normative vs. Positive Business Economics
Positive business economics studies economic facts and relationships as they are. It explains market behaviour without offering recommendations. Normative business economics uses those insights to suggest suitable actions based on business goals.
Also Read: Best Small Business Ideas for Rural Areas, Villages, Small Towns in India
The Importance of Business Economics for Management Decisions
One reason business economics is important is that it brings clarity to complex decisions. It helps managers examine pricing, costs and competition with evidence rather than assumption.
With tools such as forecasting and cost–benefit review, they can assess alternatives more carefully and move forward with greater confidence.
How Hero Fincorp Utilises Economic Principles in its Business
Economic principles influence several areas of Hero Fincorp’s operations. When designing financial products, the company studies who its customers are, what the demand looks like and what the costs involved will be.
Changes in interest rates, economic conditions and repayment patterns are reviewed regularly. This helps balance expansion with sensible risk control.
Demand analysis supports product development, and cost evaluation informs pricing decisions. Capital allocation, credit checks and portfolio review are also guided by economic reasoning.
Through this consistent use of economic analysis, Hero Fincorp works to provide competitive financial solutions while maintaining financial discipline and responsible lending standards.
If you are planning to borrow, you can explore Hero Fincorp’s loan options or use the eligibility calculator to see where you stand.
Also Read: What is Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)?
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary objective of Business Economics?
The main aim of business economics is to support sound decision-making. It uses economic reasoning when dealing with pricing, production, costs and profit planning so that choices are more considered and effective.
How does Business Economics differ from traditional Economics?
While traditional economics deals with broad economic trends, business economics works at the company level. It applies economic reasoning to practical matters like pricing and resource use.
Which tools are commonly used in Business Economics for analysis?
Typical tools include demand studies, cost comparisons, marginal calculations, break-even checks and forecasting techniques. They help managers look at different choices more clearly.
Can Business Economics predict future market trends accurately?
It cannot predict the future with complete accuracy. However, it uses data and forecasting tools to make informed estimates that support planning.
Is Business Economics only relevant for large corporations?
It is useful for businesses of all sizes. Any organisation making decisions about costs, pricing or investment can apply it.
How does scarcity relate to business decisions in Business Economics?
Scarcity means resources are limited. Businesses must decide how to use capital, labour and materials carefully to get the best possible results.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this blog post is intended for informational purposes only. The content is based on research and opinions available at the time of writing. While we strive to ensure accuracy, we do not claim to be exhaustive or definitive. Readers are advised to independently verify any details mentioned here, such as specifications, features, and availability, before making any decisions. Hero FinCorp does not take responsibility for any discrepancies, inaccuracies, or changes that may occur after the publication of this blog. The choice to rely on the information presented herein is at the reader's discretion, and we recommend consulting official sources and experts for the most up-to-date and accurate information about the featured products.