Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) - Definition and Formula

Have you ever wondered what banks do with all the money deposited by their customers? Do they have giant vaults with stacks of cash under each bank we're not aware of? The short answer is no.
Banks don't hold onto your money. They do keep a small amount with themselves for daily withdrawals. But they also give out a significant portion of them as loans.
They are, however, required to park a mandatory portion of their cash reserves with the Reserve Bank of India. The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) determines "how much" this mandatory portion is.
This post will look at what the CRR is, why it is needed, and how it impacts you.
What is the Cash Reserve Ratio?
In a nutshell, the Cash Reserve Ratio is a percentage of a bank's total deposits that should be parked with the Reserve Bank of India (RBI). This requirement was put in place under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, specifically under Section 42. It also gives the authority to change this figure at any time to maintain India's monetary stability.
The purpose of a CRR is to ensure that:
- Banks always have enough money (liquidity) to meet the demands of withdrawals.
- Banks do not over-lend to earn interest.
Also Read: Difference Between CRR and SLR
Importance and Objectives of Cash Reserve Ratio
The Cash Reserve Ratio also serves multiple purposes that go beyond ensuring banks can meet daily cash withdrawal demands. They include:
Control The Supply Of Money To Curb Inflation Or Increase Economic Activity
When excess money enters the economy, the purchasing power of the public increases. This leads to higher demand, which, in turn, increases prices of goods and services, a.k.a inflation. To combat this, the RBI can increase the CRR.
As a result, lending comes down as banks must now keep more money with the RBI as cash. This reduces purchasing power or spending, which in turn lowers demand, and as a consequence, the cost of goods and services.
Alternatively, when there is a slump in the economy, the RBI lowers the CRR. As a result, banks get more funds to lend across the board. This lowers borrowing costs for the end customers, and economic activity picks up again.
Helping Maintain Stability In The Banking System
If the CRR didn't exist, banks could leverage most of their money in a bid to earn interest. If they overleverage themselves and don't hold enough cash in reserves, they will not be able to meet their own depositors' withdrawal demands.
This can lead to a collapse of the banking sector itself, especially in times of emergencies. The CRR ensures that banks always have enough cash reserves on hand and plays a major role in enforcing discipline in the banking sector.
Support the RBI's Monetary Policy Framework
The Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) works alongside other monetary tools like the Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate to support India's economic growth. For the uninitiated, the Repo Rate is the rate at which the RBI lends money to banks when they are short of funds, and the Reverse Repo Rate is the rate at which the RBI borrows from banks.
Also Read: Difference Between Repo Rate and Reverse Repo Rate
How is the Cash Reserve Ratio Figure for Each Bank Calculated?
CRR figure for each bank is calculated by taking into account the Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL) of each bank minus the deposits it holds with other banks.
The formula is a follows: Cash Reserves to be maintained = (CRR% / 100) × NDTL
A bank's Net Demand (ND) liabilities are its:
- Current account balances
- Demand drafts
- Overdue fixed deposits
While its Time Liabilities (TL) are:
- Fixed deposits
- Recurring deposits
- Cash certificates
Let's look at this with an example: Consider a bank "X" with the following figures.
X's Demand liabilities : ₹5,000 crore
X's Time liabilities : ₹15,000 crore
Deposits with other banks: ₹2,000 crore
X's NDTL is now calculated with the formula - ND + TL - Deposits with other banks
NDTL = ₹5,000 + ₹15,000 – ₹2,000 = ₹18,000 crore
If the RBI has set the CRR at 3.75%, then based on the above formula, Bank X:
- Has to deposit 3.75% of ₹18,000 crore = ₹675 crore
- Can lend the remaining ₹18,000 - ₹675 = 17, 325 crore
What is the Current Cash Reserve Ratio in India (2025 Update)?
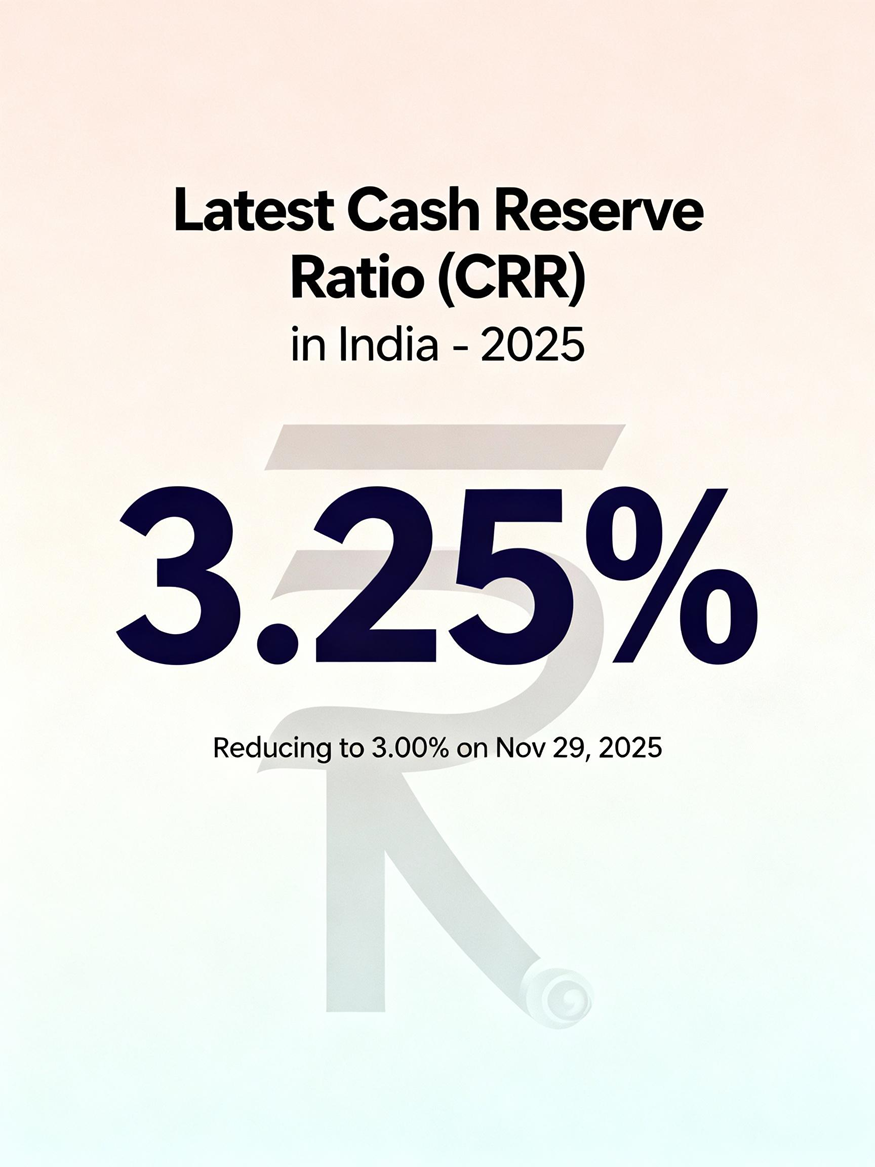
In 2025, as per RBI's circular (RBI/2025-26/46) that was sent out on the 6th of June this year, the CRR as of November 1, 2025, is at 3.25%. (It will be reduced to 3.00% on November 29th, 2025).
The RBI aims to release about Rs 2.5 lakh crore into the banking system by November 2025 to help ensure steady liquidity in the economy.
Why CRR Still Matters Today
The CRR is one of many tools the RBI leans on to sustain and maintain India's economy. For you, this means that every time you go to a bank to withdraw your own money, the banks always have the cash on hand.
Now, if you have read this post properly, you must have understood that a change in CRR (especially a reduction) will lower borrowing costs.
If you are in need of immediate funds, Hero Fincorp can lend them to you via an entirely digital application process via their instant loan app. Your application gets approved in minutes, and you get the funds disbursed to you almost always the same day.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the minimum CRR banks must maintain?
As of 29th November 2025, all banks in India will have to deposit 3% of their total cash reserves with the RBI.
2. Does CRR earn interest for banks?
Banks do not earn interest on the funds deposited with the RBI.
3. Can NBFCs be asked to maintain CRR?
As per Section 42 of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, only scheduled commercial banks need to deposit funds with the RBI at the set CRR percentage.
4. How often does RBI change CRR?
There is no set schedule to change the CRR. This is a decision made as per the current economic conditions of the country.
5. How does CRR differ from Repo Rate?
The repo rate is the rate at which a bank borrows funds from the RBI if it needs them. The CRR, on the other hand, is the percentage of a bank's total deposits that must be handed over to the RBI.
6. What happens if CRR stays low for too long?
If the CRR stays too low for too long, it leads to excessive borrowing, which ultimately drives inflation.